Electronic components require optimum cooling for the entire lifetime of the product, which is why reliability is a decisive factor in many power electronics applications. A key component for ensuring this is a heat sink that is developed specifically for each application.
In this blog article, we take a closer look at this subject.
Reliable operation is the key to the success of a system. This is particularly important in applications where it is difficult to access power electronics for maintenance purposes.
In extreme cases, there is a risk of explosion, leading to the related machine or process needing to be switched off. In addition, components located in the vicinity of the power electronics may also be damaged.
Downtime like this would mean that the system cannot be operated profitably. During downtime, there is loss of income and, depending on the application, contractual penalties may also be incurred. On top of that, complex and costly repairs would also be necessary.
Below, you will see what all this means in practice using the example of offshore wind turbines, and we will look at how to prevent malfunctions and ensure reliability by optimally cooling the power electronics using heat sinks.
Unexpected malfunctions may result in sudden overloads and high temperatures. This can happen if there is a defect in one of the electronic components. A high-quality heat sink should be able to effectively dissipate this heat. This is how it keeps the temperature within a safe range.
It needs to be matched to the power electronics components. Only then can it optimally dissipate heat and ensure safe operation of the electronics over their lifetime.
But how do they dissipate the heat emitted from electronic components? This is achieved by an optimal flow field. To ensure this, knowledge of the thermal behavior of the electronics during operation is required. The flow field (cooling structure) is then designed accordingly.
First and foremost, sufficient knowledge of power electronics is required:
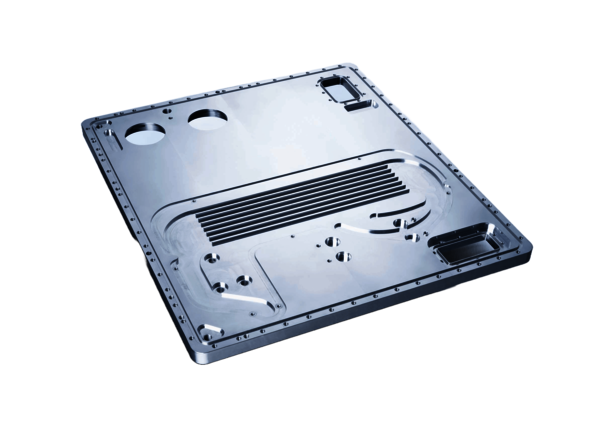
In general, vacuum-soldered heat sinks (also known as cold plates) are particularly suitable. A cold plate is a liquid-filled heat sink on which the power electronics components are mounted. Thanks to the large surface area of the connection, they ensure optimum reliability.
Read more about cold plates, how they reduce costs and extend service life in our blog article.
Offshore wind turbines in the North Sea are an example of the importance of minimizing explosion risk and maximizing reliability.
Here, electrical energy is generated as alternating current. It is converted into direct current by the converters in the converter stations of the HVDC transmission system. It is then transported over long distances to southern Germany.
In wind turbines and HVDC converter stations, the converters are cooled by vacuum-soldered cooling modules. These ensure that the electronic components in the converters and other systems are kept at optimal operating temperature.
Reliability is particularly important here because repairing offshore wind turbines is very expensive as they only be reached by helicopter, assuming the weather is good.
Failure can cause significant financial losses and repair costs. This applies in particular to power electronics applications that are difficult to access.
Offshore wind turbines in the North Sea are an example of this critical factor because they are difficult to access and repairs are expensive.
Heat sinks that are matched to the application are crucial for ensuring reliability. They effectively dissipate heat, keep the temperature stable and prevent malfunctions as a result. Vacuum-soldered cold plates are particularly reliable.
Would you like to learn more about heat sink reliability? Do you have any questions about how you can benefit from this technology in your industry?
Our service experts are here to help you.